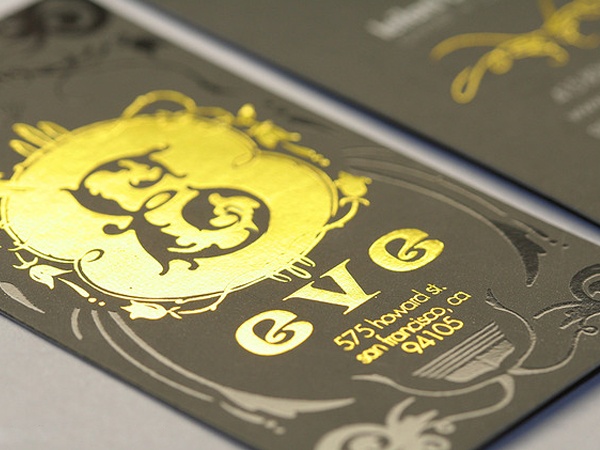
Embossing and dembossing are similar processes that create a different result. Both processes involve making a metal plate and a counter. The plate is mounted on a press and the paper is stamped between the plate and counter. This force of pressure pushes the stock into the plate, creating the impression.
Embossing produces a raised impression on your paper stock, while debossingcreates a depressed impression.
Things to remember when designing for a piece that includes embossing/debossing:
- Be aware that embossing is a mechanical process that manipulates the paper stock, so by default, it will also manipulate your design.
- Set your type with more space between letters than usual. If you put them too close to one another, they can merge and become one element once the embossing has been done. Embossing makes design elements look smaller and reduces the sharpness of smaller items.
There are two ways you can emboss your work at home: dry embossing and heat embossing.
Dry embossing, also called relief embossing, is done by tracing a stencil with some paper over it with a special tool called a stylus to get the raised effect on it.
Heat embossing, also referred to as stamp and heat embossing, is done by stamping an image on a piece of paper, sprinkling powder over the stamped image, and then applying heat.
From Amanda Woodward found on Flickr.
Silk Lamination/Lamination
Silk lamination provides a soft, silk-like finish, is water-resistant and tear-resistant, and complements vibrant colors. Pieces are traditionally printed in full-color, like any regular business card, however one additional step is taken to get their unique texture — the cardstock is coated with a durable, weather-resistant, silk laminate
finish.
Lamination can be a liquid that dries to a tough gloss or dull surface, or it can be a film. Both adhere to the surface to protect it and give it a sheen or a muted effect. The effect could be glossy, dull, or even satin (a look that’s in between glossy and dull).


Varnish
A varnish is a liquid coating applied to a printed surface to add a clear glossy, matte, satin, or neutral finish. Here are the types of varnishes:
| Varnish Type | Description |
| Gloss Varnishing | A gloss varnish gives the printed surface a glossy, sheen look. |
| Matte Varnishing | A matte varnish gives the printed surface a non-glossy, smooth look. |
| Silk or Satin Varnishing | A satin varnish gives the printed surface a neither a high gloss or matte, but the middle ground. |
| UV Varnishing | Ultraviolet (UV) varnishing is a process for achieving an even more striking type of coating on your printed material. |
| All-over UV varnish | Simply put, this is a UV seal applied all over the printed surface. |
| Spot UV Varnish | A spot varnish is applied to chosen spots (areas) of a printed piece. This has the affect of highlighting and drawing attention to that part of the design. |
Foil
To get the gold /silver stamp, a foil layer is affixed to a certain material by a heating process. It isn’t too complicated of a process and getting the files ready are quite similar to uv-spot printing. See my guide on preparing files for print as a reference and talk with your printer about how to supply the files. Foil printing normally requires vector images and/or outlined fonts of what you want to have stamped.
Thermography
Thermography produces raised printing similar in appearance to engraving, but using a different process for attaining the effect.
In thermography, a special powder is added to the ink that is to be printed on the paper. The printed piece is heated, causing the powder and ink mixture to dry, which in turn results in a raised effect on the paper.
From Demetrio Mancini
Die Cut
Die cut involves cutting irregular shapes in paper or paperboard using a die. A die can be used in printing for cutting, scoring, stamping, embossing and debossing. Dies are normally custom pieces, but your printer will usually have some standard dies (such as for rounded corners) available if you don’t need a custom template; check with your printer to see what they have — it may help reduce the cost of printing a special piece.


Letterpress
Letterpress is the oldest printing process. In this method, a surface with raised letters is inked and pressed to the surface of the printing substrate to reproduce an image in reverse.
Typically, metal type has been used, but other possibilities include carved wood or stone blocks. Most popularly used on wedding invitations, this process can also be used to create unique business cards as well as other custom printed products.

From iglooletterpress.com

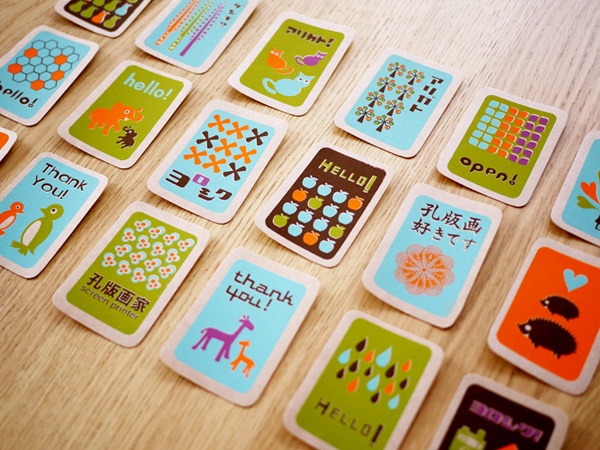
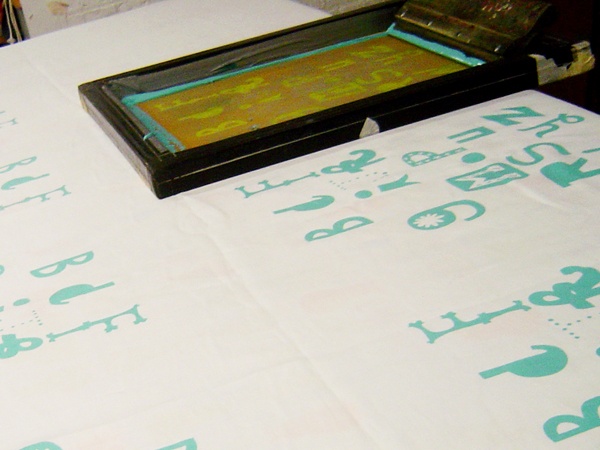
Silk Screening
Screen printing is a printing technique that uses a woven mesh to support an ink-blocking stencil. The attached stencil forms open areas of mesh that allows ink to transfer onto the material. A roller or squeegee is moved across the screen stencil, forcing or pumping ink past the threads of the woven mesh in the open areas.
From PataPri
From PataPri
From PataPri
Printing Technique Summary Table
Here are the 8 printing techniques mentioned in this guide.
| Printing Technique | Description |
| Embossing/Debossing | Embossing creates a raised impression on stock, debossing creates a depressed impression on stock. |
| Silk Lamination/Lamination | Silk lamination provides a soft, silk-like finish, is water-resistant, is tear-resistant, and complements vibrant colors. The effect could be glossy, dull, or satin. |
| Varnish | A varnish is a liquid coating applied to a printed surface to add a clear glossy, matte, satin, or neutral finish. |
| Foil | A foil layer is affixed to a certain material by a heating process. |
| Thermography | Thermography produces raised printing similar in appearance to engraving. |
| Die Cut | Die cut involves cutting irregular shapes in paper or paperboard using a die. |
| Letterpress | A surface with raised letters is inked and pressed to the surface of the printing substrate to reproduce an image in reverse. |
| Silk Screening | A printing technique that uses a woven mesh to support an ink-blocking stencil. The attached stencil forms open areas of mesh that allows ink to transfer onto the material. |

 English
English Chinese
Chinese